Researchers from Harvard Medical School & the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have shown that exercise can produce a hormone in the body that can lessen the susceptibility to obesity and diabetes and other health issues.
Mouse & human muscle tissue was tested, with the scientists charting how muscles cells can communicate with other cells in the body - particularly fat cells - and alter the biochemistry of the body after exercising.
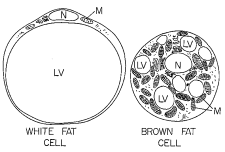 |
| LV = Lipid Vacuole |
This hormone acts on white adipose (fat) cells, turning a development of brown-fat-like cells. Brown fat is more physiologically desirable than inert white fat calls, as they require energy & use oxygen: they burn calories! That this also happens to the deep fat around the organs is also important in health. Until 2009, the assumed logic was that brown fat was in far greater quantities in babies than adults, but now it appears that irisin (potentially exercise-induced irisin) can be seen in older humans.
 |
| Brown Fat Cell |
Furthermore, rodent studies that have shown that irisin injected into white fat cells do indeed turn brown, and that glucose-tolerance was improved despite a high-fat diet. Human study participants whom volunteered for a jogging programme demonstrated higher levels of irisin after the programme finished than beforehand.
Key message? Physical activity increases irisin levels in healthy people & changes fat cells from white to brown as a result.
Exercise: All Good!
Here are some details:
A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis
- Nature
- (2012)
- doi:10.1038/nature10777
- Received
- Accepted
- Published online
Exercise always have a good impact on our lives. Researches could get any proof against the negatives.
ReplyDeletePain treatment clinic houston